- info@prototypeshlh.com
- +86-133-9285-9203
- Room 2003, 20th Floor, Xingji Building, Shangde Road, Shajing Street, Bao'an District, Shenzhen
SERVICES

CNC Machining Service
Tight tolerances and finishing capabilities, as fast as 2 days.

Vacuum Casting Service
Production quality parts without the tooling investment.

Sheet Metal Fabrication
Experience the versatility 6 cost efficiency withflexible application options.

Die Casting Service
Create high quality custom mechanicals withprecision and accuracy.

Injection Molding Service
Production-grade steel tooling, as fast as weeks.
Carbon Fiber Manufacturing
Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics are highly versatile and efficiert materials.
Popular Services

Injection Molding Service
A faster, easier way to order high-quality injection molded parts that accelerates iteration, testing, and scaled production. Upload your designs for DFM feedback and pricing in 24 hours.

3D Printing Service
Our 3D printing solutions cater to personalised needs with a diverse range of materials and colour options, including SLA, SLS, FDM, Projet, DMLS, and MJF printing services.

Surface Finishing
The easiest way to source your custom parts, with 15+ surface finishing options.
Design Guide
In-depth design guides full of best practices for all of HLH's manufacturing processes.

Case Studies
Success stories from innovativecompanies using HLH.

Blog
lndustry trends, company news andproduct updates.
Featured Posts

Aerospace & UAV
HLH is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Products
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Products.

Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive.

Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?

Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.

Communications
We understand the demands and ever changing landscape of the communications industry.

Product Development
Industrial design and engineering consultancies are some of the most innovate and creative enterprises on the planet.
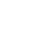
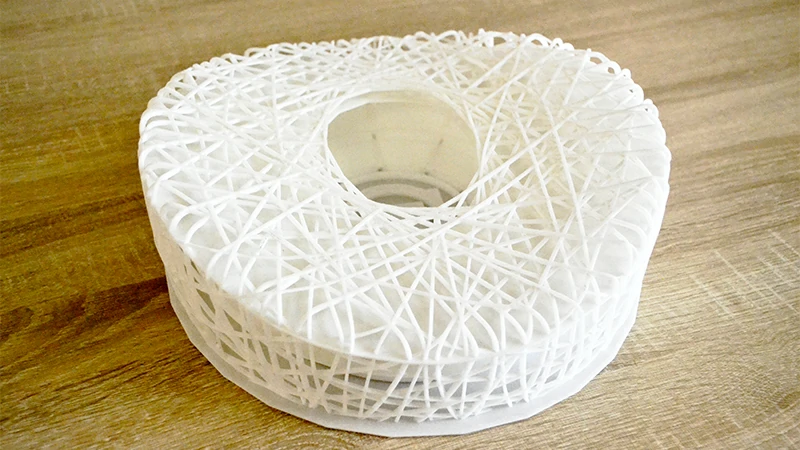
Designing a 3D model that prints accurately isn’t just about exporting your CAD file and hitting “print.” If you're aiming for high precision—especially when parts need to fit together or meet tight specs—you’ll want to pay attention to design, settings, and materials. Here’s your practical guide to crafting dimensionally accurate 3D-printed parts.

| Step | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Calibrate printer regularly | Ensures dimensional consistency across prints |
| Design with realistic tolerances | Avoids fittings that are too tight or too loose |
| Use iterations + testing | Helps fine-tune fit in real-world scenarios |
| Match method to need | SLA for fine detail, FDM for robustness or cost-effectiveness |
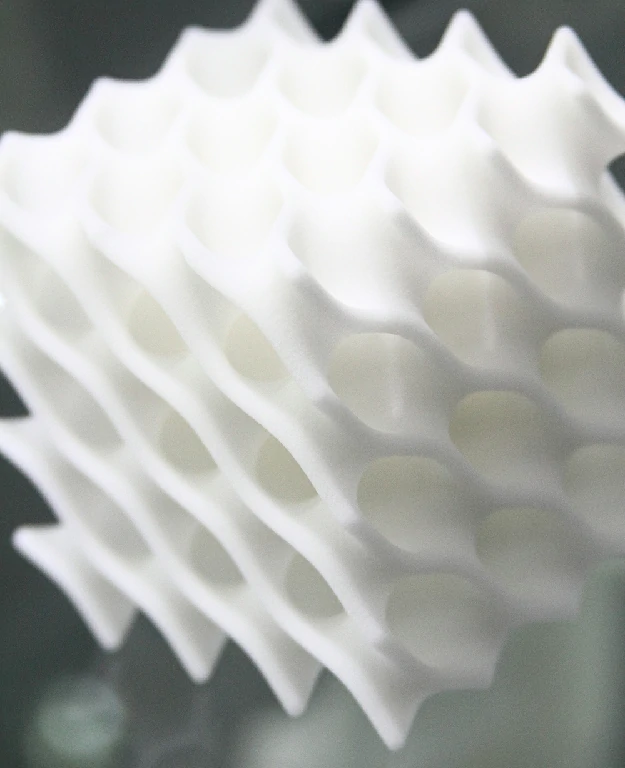
Designing dimensionally accurate 3D prints is a mix of thoughtful CAD work, smart calibration, material knowledge, and plenty of test prints. Keep iterating and refining—your parts will fit better, function more reliably, and look more professional.
If you have 3D printing requirements, please let us know and get a free quote from us. View our 3D printing services - We have the easiest way to source high-quality 3D printed prototypes and production parts. ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and AS9100 certified.